School Function Assessment Template
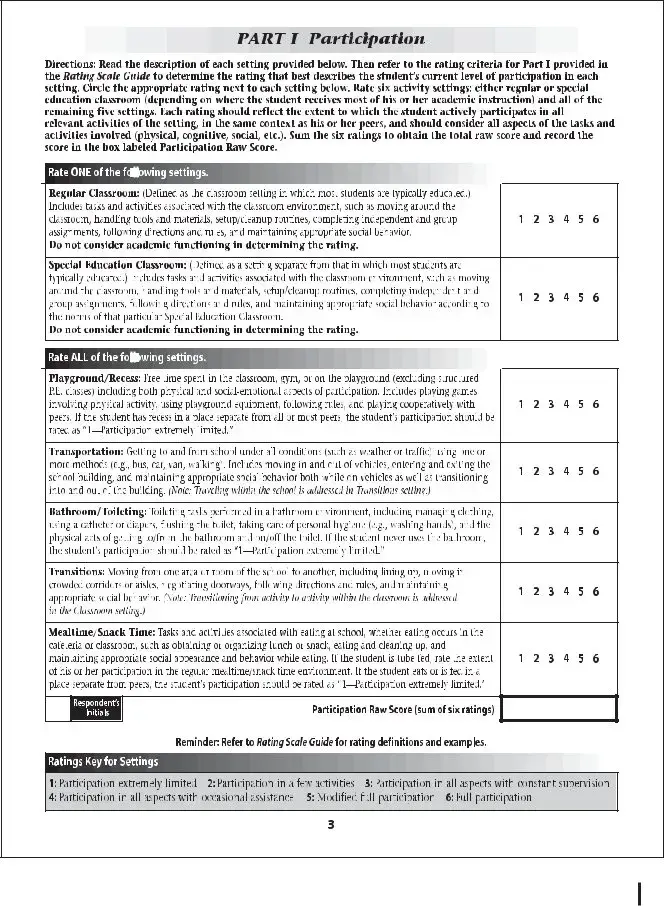
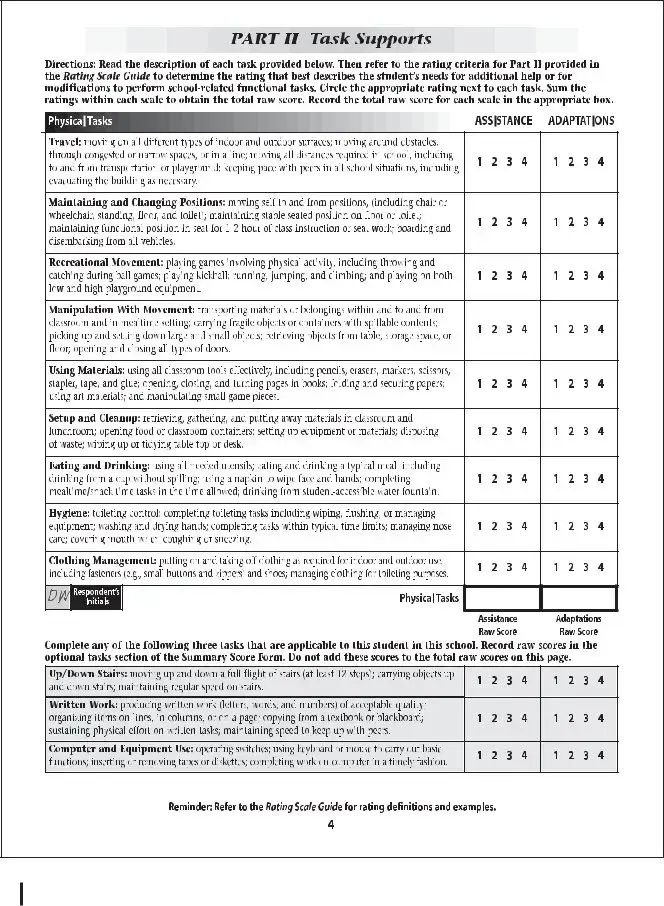
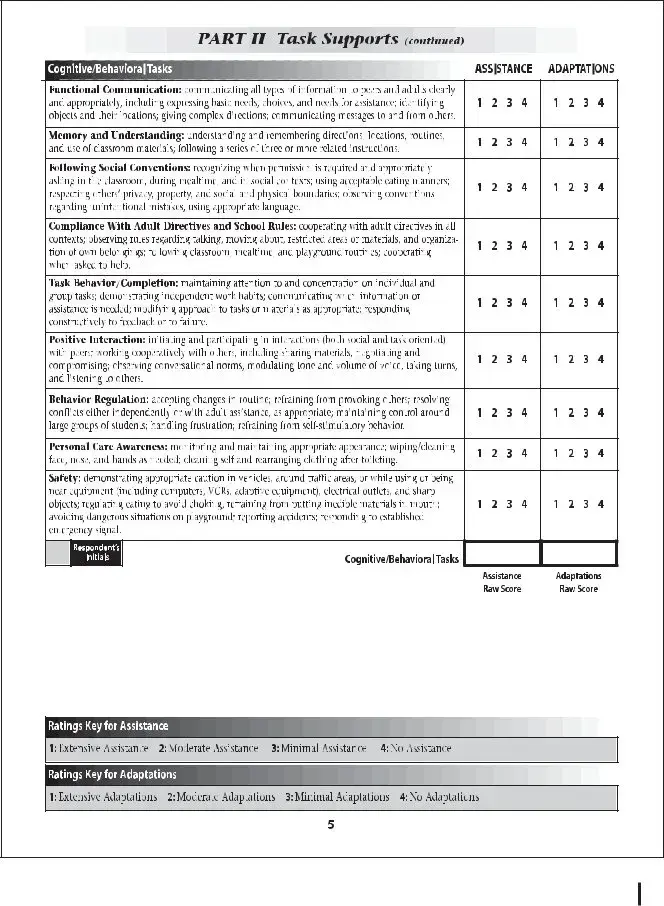
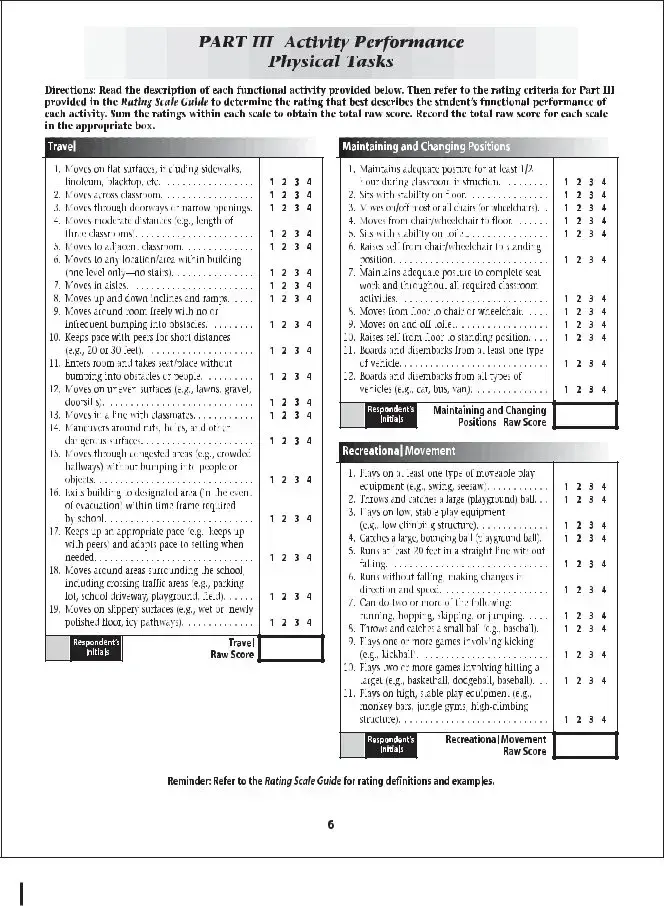
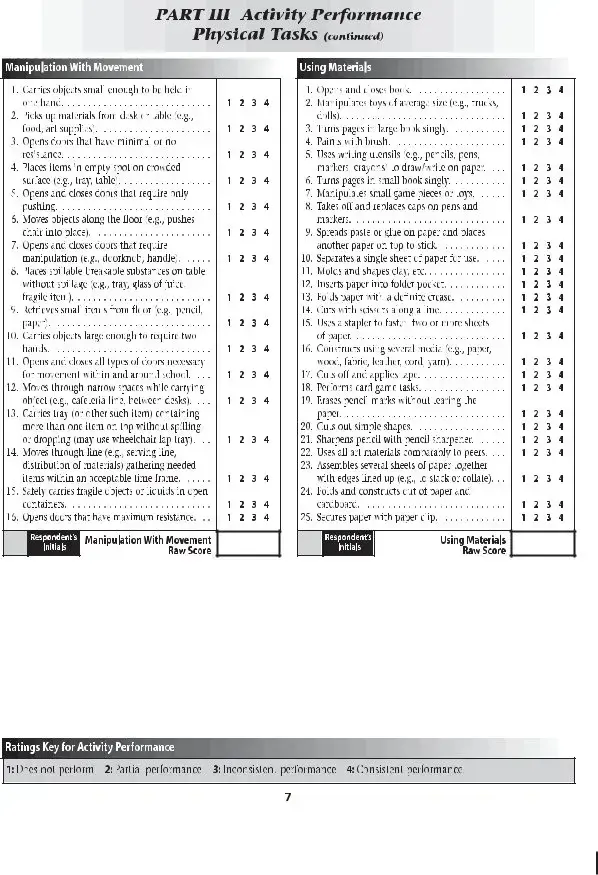
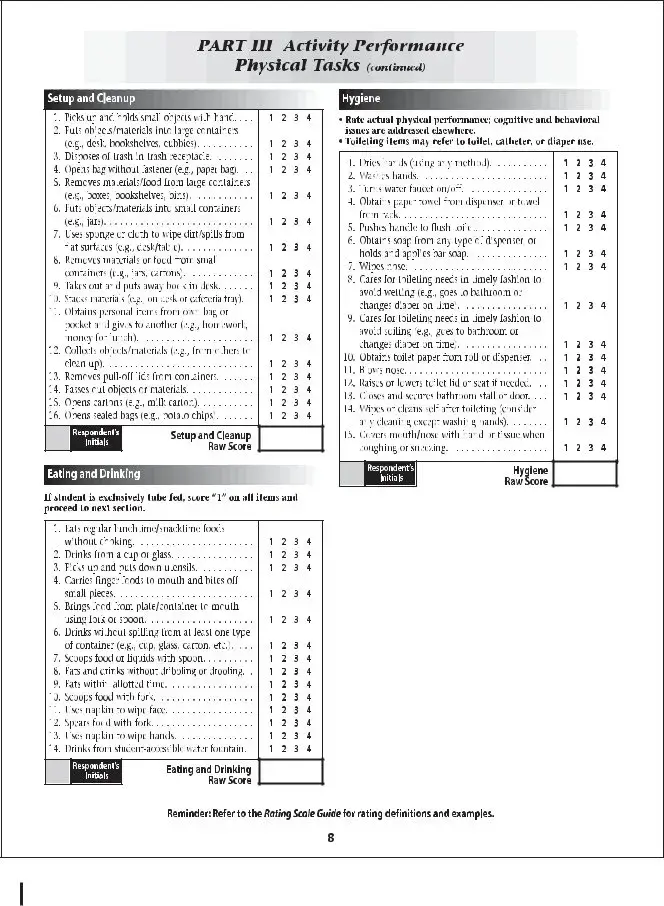
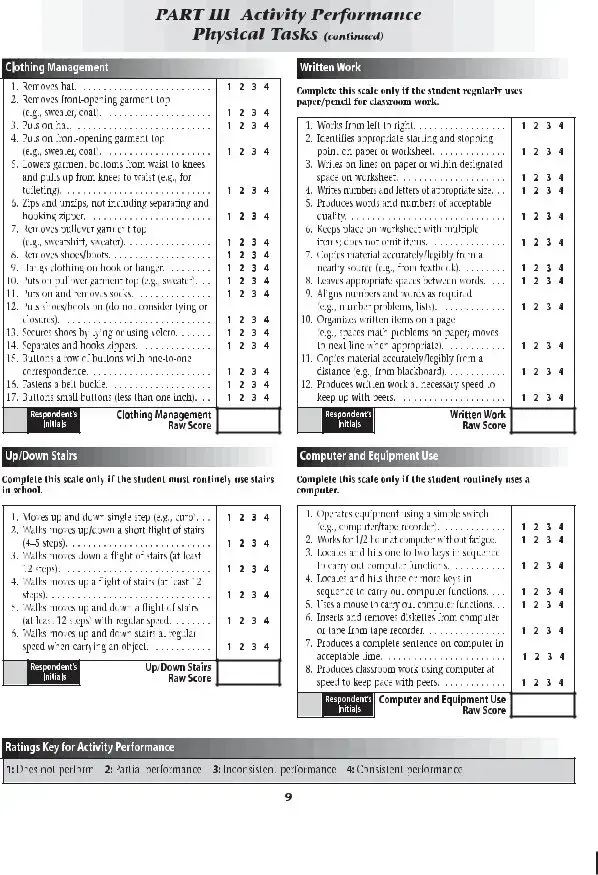
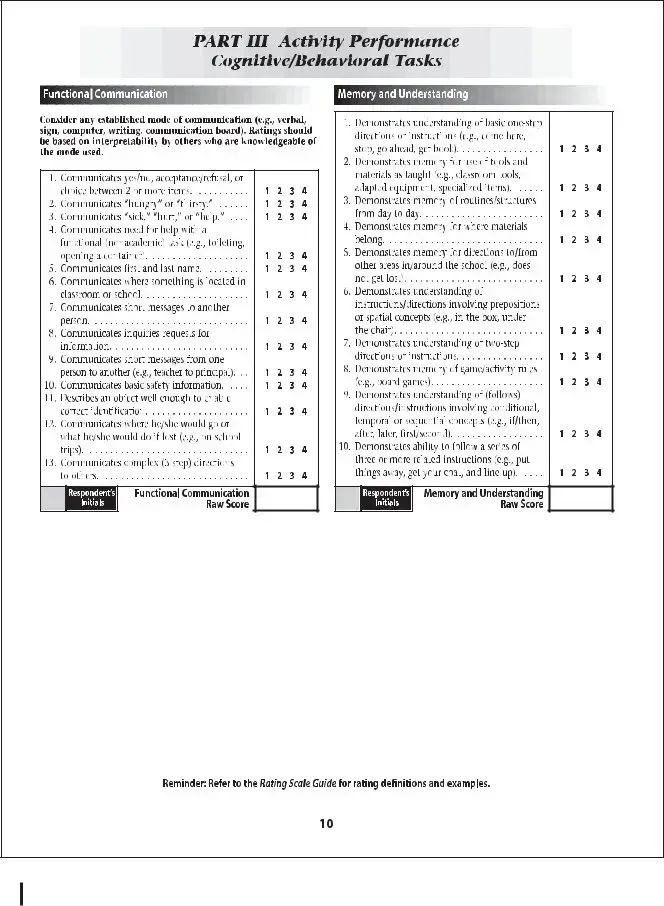
The School Function Assessment form is a tool designed to evaluate a student's performance in various school-related activities. This assessment helps educators and parents understand how well a child can participate in daily school functions and identify areas that may need support. By focusing on the child's abilities and challenges, the form aids in creating effective educational strategies tailored to individual needs.
Launch School Function Assessment Editor

School Function Assessment Template
Launch School Function Assessment Editor

Launch School Function Assessment Editor
or
⇓ PDF Form
Complete the form at your pace — fast
Finish your School Function Assessment online and download the final version.